setw()
function is used to create the specific width of empty space or empty
gap space like tab, in between the sentences or in function
headings.The function header library that is used for this function
is "iomanip".
Let
us have a look through an example :
Here the cout statement first
prints the hello word and then it leaves the space of 10 characters.
After that we have again an another word to be printed. So the
compiler checks the no of characters (sizeof the word) and will
initialize the remaining space for the gap, printing the word
starting from the last space of gap right to left. If the word will
have greater number of characters than the size specified for the
gap then it starts printing next after the first word without space.
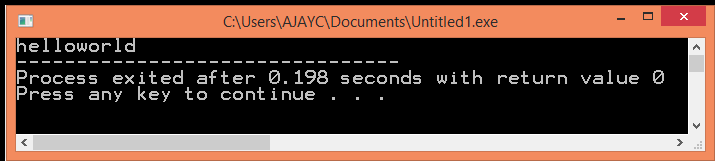
cout<<"hello"<<setw(10)<<"world";
Output :
cout<<"hello"<<setw(4)<<"world";
Here the size of word "world"
is greater than the size specified for the empty width.
Output :